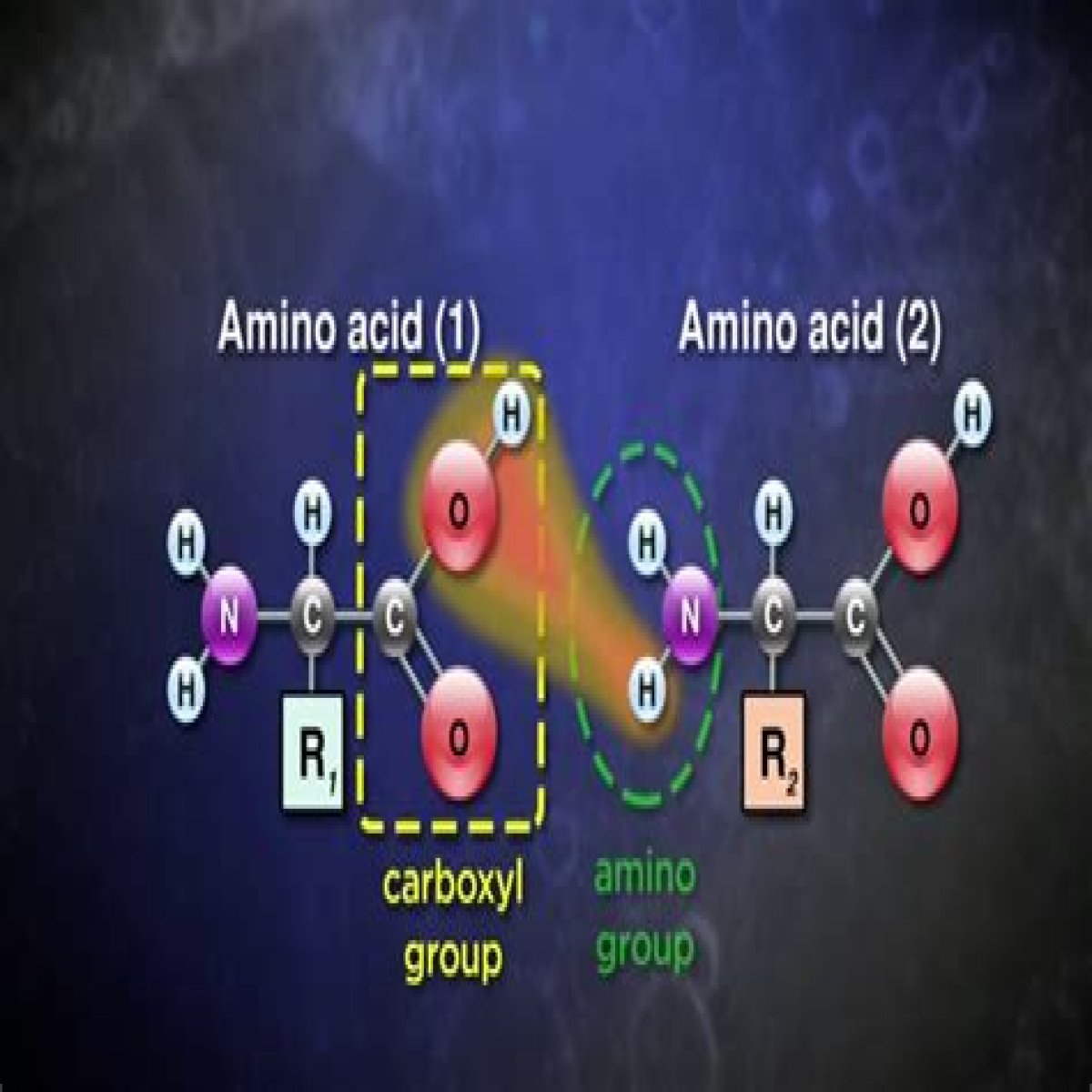
Amino acids are the fundamental building blocks of proteins, playing a critical role in various biological processes. They are organic compounds composed of an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a distinctive side chain. The polarity of amino acids, which refers to the distribution of electrical charges across their molecules, is a significant factor that influences their behavior and interactions in biological systems. Understanding amino acids polarity is essential for grasping how proteins fold, function, and interact within living organisms.
Amino acids can be classified based on their polarity into three main categories: nonpolar, polar, and charged. This classification is crucial in determining how they interact with each other and with other molecules, such as water and lipids. For instance, nonpolar amino acids tend to be hydrophobic, meaning they repel water, while polar and charged amino acids are hydrophilic, allowing them to interact favorably with water. This property is vital for the proper folding and stability of proteins, which ultimately dictates their function.
The study of amino acids polarity not only enhances our understanding of protein structure and function but also aids in various applications, including drug design, biotechnology, and disease treatment. By examining how different amino acids behave in various environments, scientists can develop better strategies for modifying proteins, designing new medicines, and understanding the biochemical pathways of life. As we delve deeper into the concept of amino acids polarity, we uncover the intricate web of interactions that sustain life on Earth.
What is Amino Acids Polarity?
Amino acids polarity refers to the distribution of electrical charges within an amino acid molecule. This property can influence how amino acids interact with one another, as well as with other molecules in biological systems. Polarity is determined by the presence of various functional groups in the amino acid's side chain, which can either attract or repel water molecules.
How Are Amino Acids Classified Based on Polarity?
Amino acids can be categorized into three main groups based on their polarity:
- Nonpolar Amino Acids: These amino acids have hydrophobic side chains that do not interact favorably with water. Examples include alanine, valine, and leucine.
- Polar Amino Acids: These amino acids possess side chains that contain polar groups, allowing them to interact with water. Examples include serine, threonine, and asparagine.
- Charged Amino Acids: These amino acids have side chains that carry a positive or negative charge, making them highly polar and hydrophilic. Examples include lysine (positively charged) and aspartic acid (negatively charged).
Why is Amino Acids Polarity Important for Protein Structure?
The polarity of amino acids plays a crucial role in protein folding and stability. Proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids that fold into specific three-dimensional shapes, which are essential for their function. The interactions between polar and nonpolar amino acids help stabilize these structures. For instance, nonpolar amino acids tend to cluster together in the interior of proteins, away from the aqueous environment, while polar and charged amino acids are often found on the surface, interacting with the surrounding water.
How Does Amino Acids Polarity Affect Enzyme Function?
Enzymes are specialized proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions. The polarity of the amino acids that make up an enzyme can significantly impact its active site, where the substrate binds. An enzyme's active site often contains a mix of polar and nonpolar amino acids, which can create a suitable environment for substrate binding and catalysis. This balance of polarity allows for the precise positioning of substrates and the stabilization of transition states during the reaction.
Can Amino Acids Polarity Influence Drug Design?
Yes, the polarity of amino acids is a critical consideration in drug design. Understanding how amino acids interact with each other and with potential drug molecules can help researchers develop more effective pharmaceuticals. For example, drugs that target specific proteins must be designed to fit into their active sites, which are influenced by the polarity of the amino acids present. By manipulating the polarity of amino acids in drug molecules, scientists can enhance their efficacy and selectivity.
What Role Does Amino Acids Polarity Play in Disease Mechanisms?
Amino acids polarity can be linked to various disease mechanisms. Mutations in genes encoding proteins can lead to changes in amino acid composition, affecting the polarity of the resulting protein. These changes can disrupt normal protein folding and function, potentially leading to diseases such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and various neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding these relationships can aid in the development of targeted therapies.
What Are Some Key Takeaways About Amino Acids Polarity?
- Amino acids polarity is crucial for protein structure, function, and interactions.
- Amino acids can be classified into nonpolar, polar, and charged categories based on their polarity.
- The polarity of amino acids influences enzyme activity and drug design.
- Changes in amino acid polarity can be linked to various diseases, highlighting its importance in biomedical research.
Conclusion: The Significance of Amino Acids Polarity in Biology
In conclusion, amino acids polarity is a fundamental concept that underpins our understanding of protein structure and function. By exploring the interactions between different types of amino acids, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms of life and the underlying causes of various diseases. As science continues to advance, the study of amino acids polarity will remain a vital area of research, with implications for biotechnology, drug development, and our understanding of biological processes.
Exploring The Mystique Of Hades EpithetsDiscovering The Height Of Donald Trump In CentimetersEmbracing The Essence Of Freedom Naturist Living
Do hydrophobic amino acids hydrogen bond publishingnaxre
Why are there 20 amino acids? Feature Chemistry World
Amino Acids Physical Properties, Structure, Classification, Functions